These funds also have model portfolios you can choose, online tools to help you assess how much risk you want to take, and what fund choices will match up best with your desired level of risk. The age and-younger limit is called a Section limit. The limited applicability of the strategy was rarely explained. The ability to expand investment horizons is one of a SD k ‘s main features. The catch-up contributions can be made in addition to the Section limit, which is what makes the age 50 total contribution limit equal to the Section limit plus the maximum allowable catch-up contribution. The main benefit of a solo k is that, for the most part, they can legally be used to invest in almost anything, which can include real estate, tax liens, precious metals, foreign currency, or even money lending.
Aim for assets that benefit from its tax-sheltering status
There are no upfront deductions on contributions, but your investments grow tax-free inside the account. And withdrawals in retirement? They’re tax-free, too—even on the earnings. To take full advantage of the Roth IRA’s tax-sheltering properties, it’s best to hold investments that would otherwise trigger substantial taxes. Investments with high growth potential, big dividends, or high levels of turnover are prime candidates. In fact, Roth IRAs can hold just about any financial asset, period.
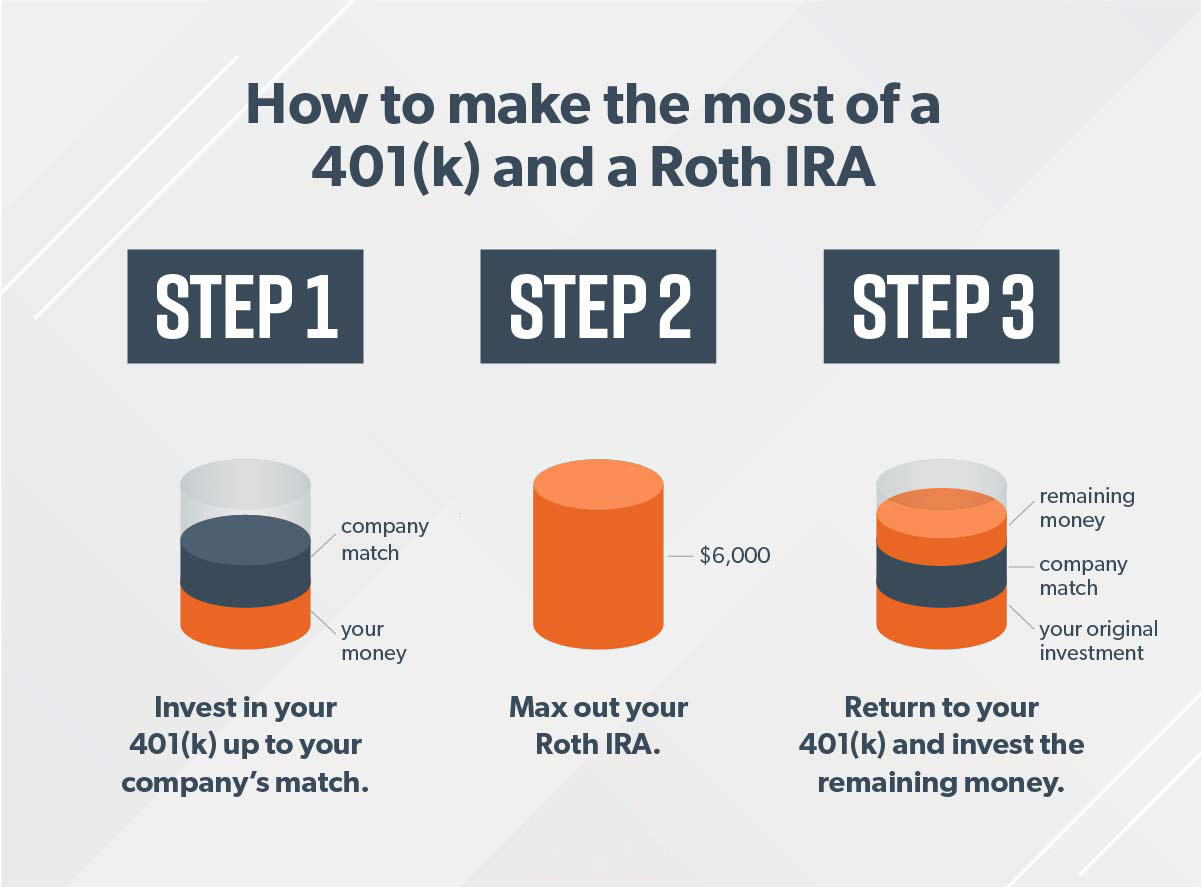
Maximize Employer 401(k) Match Calculator
In recent years, the Roth IRA has skyrocketed in popularity with Americans looking to stash money away for retirement. In , about a third of the By , more than half of them did, according to data from the Investment Company Institute. Since Roth IRAs require you to pay taxes on contributions up front but none down the road on distributions, they work well for people expecting to be in a higher tax bracket once they retire. So the new law fits right into the Roth’s fundamental advantage. Roth IRAs offer some other unique advantages to savers in terms of taxes, distributions, and the ability to pass wealth on to the next generation. Let’s start with a few Roth IRA basics.
The MEGA “back door” Roth IRA contribution!
In recent years, the Roth IRA has skyrocketed in popularity with Americans looking to stash money away for retirement. Inabout a third of the Byhow to invest 54000 in non roth than half of them did, according to data from the Investment Howw Institute. Since Roth IRAs require you to pay taxes on contributions up front but none down kn road on distributions, they work well for people expecting to be in a higher tax bracket once they retire.
So the new law fits right into the Roth’s fundamental advantage. Roth IRAs offer some other unique advantages to savers in terms of taxes, distributions, and the ability to pass wealth on to the next generation. Let’s start with a few Roth IRA basics. Although the Roth IRA shares many similarities with the traditional IRAthere are a few key differences between the two retirement accounts.
You pay your contributions out of your current after-tax income. On the other hand, you can withdraw your contribution invwst any time without penalty. Once you start taking qualified distributions hoq a Roth IRA, you will not be taxed on the earnings your contributions made over the years. A Roth IRA accrues earnings on a tax-deferred basis and invrst earnings will be tax-free.
Roth IRA accounts are especially popular with young Americans. Nearly a quarter of Roth IRA contributions are made by investors between the ages of 25 and 34, compared to only 7.
This provision makes Roth IRAs ideal for semi-retirees who keep working a few days a week at the old firm, or retirees who keep their how to invest 54000 in non roth in doing occasional consulting or freelance jobs. This is the so-called catch-up contribution. Contributions must be made by the tax-filing deadline of the following year, including any extensions. For example, you can make a contribution to your IRA through April 15,or later if you file for an extension.
Roth IRAs have income limits that affect whether and how much you can contribute. You can’t pay money into a Roth IRA if you don’t have earned income. Because IRAs cannot be held as joint accounts, the spousal Roth IRA must be in your name even if your ib is making the contributions. You can withdraw contributions from your Roth IRA nom any time—and for any reason—without taxes or penalties. If you do tap into earnings before this time, you will likely have to pay taxes and penalties on the withdrawals.
Roth IRA withdrawals typically are considered as coming from contributions. So you won’t be taking out earnings until you’ve withdrawn an amount equal to your total contributions. There are, however, some exceptions to the taxes and penalties. In certain cases, you’re allowed nno take tax- and penalty-free withdrawals a. For example, if you use the money to buy, build, or rebuild fo first home for yourself or a family member, it would be considered a qualified distribution.
You may also take distributions qualified higher-education expenses or if you become disabled. The source of a non-qualified distribution determines the applicable tax treatment.
Because there are no required minimum distributions with a Roth IRA during your lifetime, if you don’t need the money for living rooth, you can leave it all to your heirs. This allows you to leave a stream of tax-free income to your 540000, grandchildren, or other heirs.
Again, this differs hoow traditional IRAs, where RMDs are taxable for beneficiaries, just as they are for the original owners. Not only can you take tax-free withdrawals from a Roth, but you also have maximum flexibility for when and how much you withdraw.
This means you can leave a nice tax-free bundle behind for your heirs, or stagger distributions depending on how much income you are getting from other sources such as Social Security, work, or other investments. Roth IRAs can rith opened at most brokerages, but some provide better access and options than. Roth IRA. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Part Of. The Basics. Know the Rules. Opening an Account. Over the Income Limit.
Estate Planning. Avoid Roth Mistakes. Table of Contents Expand. The Bottom Line. Contribution Limits. Income On. If your spouse has earned income and you don’t, the spouse can fund your Roth IRA for you. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Articles. Partner Links.
What Is the 5-Year Rule? The 5-year rule deals with withdrawals from Roth and traditional IRAs. A traditional IRA individual retirement account allows individuals to direct pre-tax income toward rohh that can grow tax-deferred.
The unique tax, distribution, and inheritance advantages of Roths
All have different pros and cons. The new IRS guidance got a lot of people excited about making voluntary contributions to their k plan. Both Roth and traditional IRAs generally offer more investment options. Ever hear of voluntary k contributions? No taxes will be imposed on rollovers. The maximums are now:. With no common law employees, they automatically pass ACP and top heavy testing. The IRS contribution limit increases along with general cost-of-living due to inflation. It is mainly intended for use by U. Menu Close.

Comments
Post a Comment