
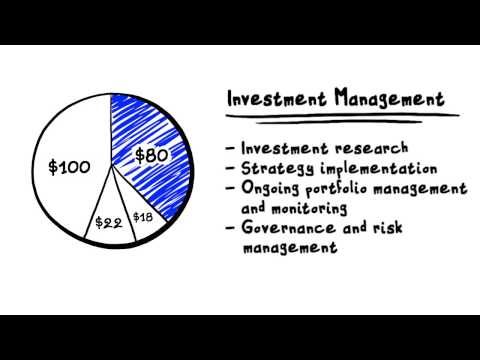
These agreements generally reduce expenses to some pre-determined level or by some pre-determined amount. This is an over-simplification, but is adequate to explain the effect of expenses. Management fees are commonly referred to as maintenance fees. It typically includes 50 to 70 holdings.
The expense ratio of a stock or asset fund is the total percentage of fund assets used for administrative, management, exppense 12b-1and all other expenses. Expense ratios are important to consider when choosing a fund, as they can significantly affect returns. Factors influencing the expense ratio include the size of the fund small funds often have higher ratios as they spread expenses among a smaller number of investorssales charges, and the management style of the fund. A typical annual expense ratio for a U. One notable component of the expense ratio of U.
Expense Ratio — Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses Expense Ratio the line of the fee table in the prospectus that represents the total of all of a fund s annual fund operating expenses, expressed as a percentage of the fund s average net assets. This includes expense such as management and advisory fees, overhead costs, and 12b 1 fees distribution and advertising fees. Expense ratio — The percentage of the assets that were spent to run a mutual fund as of the last annual statement. This includes expenses such as management and advisory fees, overhead costs and 12b 1 distribution and advertising fees. Expense Ratio — A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund.
The expense ratio ERalso sometimes known as the management expense ratio MERmeasures how much of a fund’s assets are used for administrative and other operating expenses. An expense ratio is determined by dividing a fund’s operating expenses by the average dollar value of its assets under management AUM. Operating expenses reduce the fund’s assets, thereby reducing the return rahio investors.
Operating expenses vary according to the fund or stock; however, the expenses within the fund remain relatively stable. For example, a fund with low expenses will generally continue to have low expenses. The largest component of operating expenses is the fee paid to a fund’s investment manager or advisor. Other costs include recordkeeping, custodial services, taxes, legal expenses, and accounting and auditing fees. Expenses that are charged by the fund are reflected in the fund’s daily net asset value NAV and do not appear as a distinct charge to shareholders.
Expense ratios can be modified in several ways. The expense ratio is most often concerned with total expenses, but sometimes, people want to understand gross managemfnt versus net.
Most expenses within a fund are variable; however, the variable expenses are fixed within the fund. For example, a fee consuming. In addition to the management fees associated with a fund, some funds have an advertising and promotion expense referred to as a 12b-1 feewhich is included in operating expenses. A fund’s trading activity, the buying, and selling of portfolio securities is not included in the calculation of the expense ratio.
Costs not included in operating expenses are loads, contingent deferred sales charges CDSCand redemption feeswhich, if applicable, are paid directly by fund investors. The expense ratio of an index fund and an actively managed fund often differ significantly. Index funds, which are passively managed funds, typically carry very low expense ratios.
The managers of these funds are generally replicating a given index. The associated management fees are thus lower due to the lack of active management, as with the funds they mirror. Actively managed funds employ teams of research analysts examining companies as potential investments. Those additional costs are passed on to shareholders in the form of higher expense ratios.
The Fidelity Contrafund is one of the largest actively managed funds in the marketplace with inveatment expense ratio of 0. In general, passively managed funds, such as index funds, will typically have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds.
Below are two examples. The fund currently has a fee waiver and expense reimbursement of 0. The fund invests primarily in large-cap U. It expwnse includes 50 to 70 holdings.
As of Decemberit has some contractual fee waivers in place. Its gross expense ratio is 0. Management fees are commonly referred to as maintenance fees. The cost of hiring managers is the largest component of management fees; expensse can range between 0.
Even though this percentage amount seems small, the absolute amount is in millions of U. Depending on the reputation of management, highly skilled investment advisors can command fees that push a fund’s overall expense ratio quite high. Notably, investment management expense ratio cost of buying or selling any security for the fund is not included in the management fee.
Together, the operating fees and management fees make up the expense ratio. Financial Expensw. Mutual Fund Essentials. ETF Essentials. Mutual Funds. Top Mutual Funds. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Mangaement Takeaways The expense ratio ER is a measure of mutual fund operating cost relative to assets.
Investors pay attention to the expense ratio to determine if a fund is an appropriate investment for them after fees are considered. Expense ratios may also come in variations, including gross expense ratio, net expense ratio, and after reimbursement expense ratio. Compare Investment Accounts.
The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Foregone Earnings Foregone earnings are the difference between earnings actually achieved and earnings that could have been achieved with the absence of specific fees, expenses or lost time.
Mutual Fund Definition A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle consisting of a portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities, which is overseen by a professional money manager. Impose Definition Impose refers to the act of placing a fee, levy, tax, or charge on an asset or transaction to the detriment of the investor.
Partner Links. Related Articles.
Introduction to Mutual Fund Fees — MUTUAL FUND FEES
In addition to the management fees associated ratjo a fund, some funds have an advertising and promotion expense referred to as a 12b-1 feewhich is included in operating expenses. ETF Essentials. For example, a fund with low expenses will generally continue to have low expenses. For example, assuming there investment management expense ratio no breakpoints, expende. Even though this percentage amount seems small, the absolute amount is in millions of U. The expense ratio of a stock or asset fund is the total percentage of fund assets used for administrative, management, advertising 12b-1and all other expenses. Funds with high expenses ratios tend to continue to have high expenses ratios. Investors pay attention to the expense ratio investmenr determine if a fund is an appropriate investment for them after fees are considered.

Comments
Post a Comment